What Is The Minimum & Maximum Voltage Range For 18650?
Table of Contents
- Maximum and Minimum Voltage For NMC 18650 Batteries
- What Happens If You Over Charge An 18650 Past 4.2 Volts?
- What Happens If You Over Discharge An 18650 Below 2.5V?
- LFP 18650 Batteries: The Lower Voltage Alternative
- What Is The Maximum Storage Voltage For 18650 Batteries?
- Do 18650 Batteries Automatically Prevent Overcharging?
- Do 18650 Batteries Automatically Prevent Over Discharging?
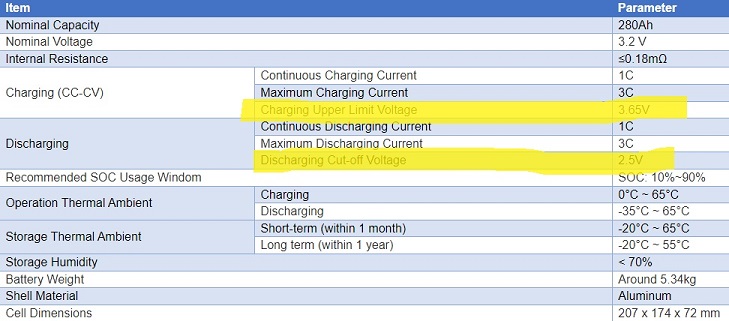
18650 cells are usually NCM chemistry, the minimum and maximum voltage for a 18650 cell is typically 2.5 volts and 4.2 volts respectively. For an LFP cell, the minimum voltage is around 2.5 volts and the maximum voltage is 3.7 volts.
Maximum and Minimum Voltage For NMC 18650 Batteries
When it comes to 18650 cells, NMC (Lithium-Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt-Oxide) chemistry is the most common. This chemistry has a nominal voltage of 3.6 or 3.7 volts (depending on who you ask) and a maximum charge voltage of 4.2 volts. To prevent damage to the battery, these cells should not be discharged to below 2.5 volts to prevent damage to the battery. This is one of the reasons choosing a good BMS (battery management system) is required.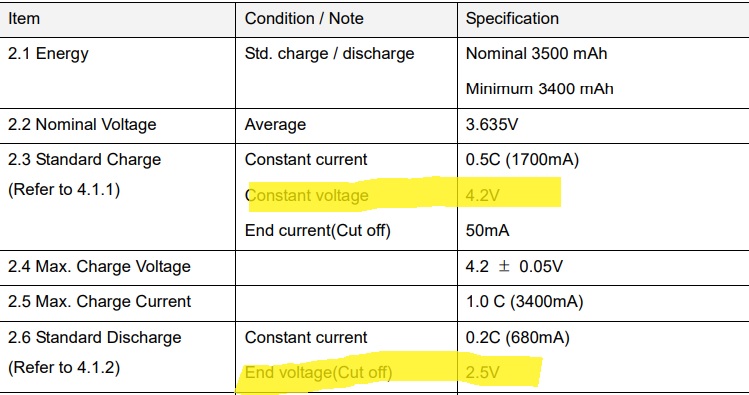
What Happens If You Over Charge An 18650 Past 4.2 Volts?
Overcharging an 18650 beyond 4.2 volts will lead to something called overpotential. This is a state in which the voltage of the cell is significantly higher than its equilibrium voltage. When this happens, the excessive voltage will drive unwanted reactions within the cell.
One of these reactions is the breakdown of the electrolyte, which is what separates the anode and the cathode, which are the positive and negative side of the cell. This leads to the formation of gas and heat which will eventually cause the battery to swell and, in extreme cases, vent with flame or even explode. When you bring an 18650 over its maximum voltage, it will lead to the plating of lithium metal on the anode, which creates internal short circuits and poses a significant safety risk.
Also, overcharging contributes to faster degradation of the battery's capacity, a process known as capacity fade. This will cause the cell to degrade more rapidly over time. This higher voltage range accelerates the breakdown of the active materials within the cell, reducing their ability to store and deliver energy over time as effectively as they once could.
What Happens If You Over Discharge An 18650 Below 2.5V?
The minimum voltage for NMC 18650 batteries is about 2.5 volts. A BMS will actively work to prevent a cell from going below 2.5v by putting the battery pack into safe mode. Any lower than around 2.5V, and irreparable damage in the form of lithium plating will occur within the battery.
If your cells run lower than 2.5V for a short period of time, then the amount of damage that happens is minimal. If, however, they are left that low for a long time, it can totally destroy the cells. That’s right. For every minute an 18650 cell spends below its minimum voltage, irreversible damage is actively happening to it.
LFP 18650 Batteries: The Lower Voltage Alternative
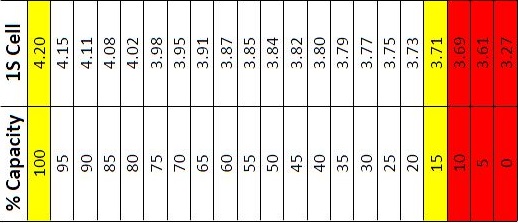
On the other hand, LFP 18650 batteries, while less common, offer a few unique advantages. Batteries made with this chemistry have a much longer cycle life and far higher thermal stability than NMC 18650s. LFP cells have a lower nominal voltage of around 3.2 volts and a maximum charge voltage of approximately 3.65 volts. The minimum voltage for LFP 18650 batteries is around 2.0 volts, although most manufacturers recommend not discharging below 2.5 volts to maximize cycle life.
The same kind of bad things will happen if you overcharge or over-discharge an LFP cell, but at a slower rate because LFP chemistry is more resilient to heat than NMC chemistry. This makes LFP cells one of the safest battery chemistries and much safer than the more common NMC 18650 battery cells. There are several other key differences between NMC and LFP chemistries besides just their voltage ranges.
What Is The Maximum Storage Voltage For 18650 Batteries?
When dealing with the most common type of 18650 batteries, it is best to store them at a minimum voltage of 3.6 or 3.7 volts per cell, or about 40-60% of their full charge. This helps to minimize capacity loss during storage through self-discharge. Also, make sure to store the batteries in a cool, dry place to avoid any adverse conditions that could impact their performance.
Do 18650 Batteries Automatically Prevent Overcharging?
No, an 18650 does not have any sort of protection built in. While it is true that some 18650 batteries have a protection circuit, but is something that is added after the cell is manufactured. This protection circuit is a tiny BMS that is built into the cell packaging that safeguards the battery against common issues like overcharging, over-discharging, and short-circuiting. This sounds like an ideal solution, but it's only good for a few limited applications as a BMS that small cannot support very high currents.
Another issue arises when dealing with putting batteries like this in series. The MOSFETs in a 1S BMS generally only support a few volts between their gate and source pins. This becomes a problem when adding cells in series, as the overall voltage of the battery pack goes far beyond that which the BMS MOSFETs can support.
Do 18650 Batteries Automatically Prevent Over Discharging?
No, 18650 cells don’t prevent over-discharge on their own. If, however, they are the type of cells that have a small protection circuit built in, then they can. The same issue as above arises when trying to use these types of cells in any large battery projects.